What Is A Risk-Based Approach To Business Cyber Security
There are fundamental aspects of cyber security, that managed technology solutions providers serving small-to-medium businesses need to understand and implement.

Here at BVA, we help businesses of all sizes and industries, who are seeking guidance and need assistance implementing sound, best practice cyber security operations, technology, and infrastructure.
We utilize aa risk-based approach to effectively and efficiently identify problems, align business objectives, and find solutions to solve for gaps in existing pillars of cyber security.
What Is A Risk-Based Approach?
Cybersecurity risk is simply defined as an effect of uncertainty on or within an information and technology environment.
We see this materialize in the loss of confidentiality, availability and integrity for our systems, devices, data, people and processes.
As we collectively become more aware of today’s technology world and increase our level of cyber security awareness, we start to ask questions around the risk to our business and the risk to others.
Cyber security awareness starts with:
- Identifying the risk across the three pillars of cybersecurity
- Understanding the threats which impact those three pillars
- Creating a gap analysis to solve for the limitations in your environment
Why Is It Important?
Once you have clearly identified the risk, you can prioritize the list and solve for the greatest likelihood and impact to the organization.
Instead of haphazardly throwing a dart at a board, you can be more precise in hitting the target.
Spend money and time on the items of importance to keep the business running, even in the event of a cyber security incident.
Risk is not the same for every business or business owner. Be careful making an assumption that one size fits all, as that is not the case.
Evaluate the following areas from the cybersecurity risks for your business first:
- Acceptable use policy
- Password policy
- Next generation firewalls
- Advanced endpoint defense
- Protective filtering
- Patch approval & management
- Data backup
- User awareness training
- Two-factor authentication
- Network assessment
- Domain Name System (DNS) security
- Dark web monitoring
Once you have everything implemented to meet your business objectives, then evaluate each of these areas for your customers in the same manner.
You will have asked yourself many of the same questions your customers are going to ask you, “Why is this important?”
You will have the answers at your fingertip since you already went through it.
Each topic is expanded with a brief definition of what it is, why it is important to address, and who are some resources that could help.
Acceptable Use Policy
What is it?
A comprehensive acceptable use policy is one of the cornerstones of an effective cybersecurity program.
It is a document that defines the do’s and don’ts while using corporate resources, i.e., information technology.
This can take on myriad forms, but it is paramount to spell things out as succinctly as possible to minimize misinterpretation and lapses in your security posture.
Why is it important?
An acceptable use policy aids in protecting from internal and external threats or mishaps.
This is done by outline or providing guidelines as to how technology, the network, and data are handled and interacted with on a continuous basis.
It also helps to define reporting and accountability measures to aid in addressing issues as they arise, so the organization can take a very proactive approach to mitigation.
The creation and acceptance of this document can serve as the framework for aiding the company in its compliance efforts related to insurance and government regulations as well.
Password Policy
What is it?
This is a written policy within the organization that defines the requirements for passwords used with the organization.
This can be enforced through technical setups using a directory service (such as Active Directory), but the written policy is designed to enforce these rules beyond what is used just for these directory services.
Why is it important?
Not all logins are controlled by the directory service logins and when new vendors are brought in, they need to be able to follow this written policy.
Follow the Sophos best practices for using strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and password managers.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
What is it?
Multi-factor authentication, MFA or 2FA, is a security process in which users provide two different authentication factors to verify themselves.
Multi- factor authentication methods usually rely on a user providing a password as the first factor and a second different factor, including:
- one-time passcode
- security key
- facial recognition
- fingerprint
Why is it important?
MFA or 2FA provides an additional layer of security to the authentication process to gain access to devices or online accounts.
If a user password is hacked, a password is not enough to gain access. It needs to be enforced to protect users’ credentials from malicious hackers.
Hackers often use phishing campaigns to steal credentials, make sure you’re aware of these techniques.
According to Microsoft, MFA can prevent 99.9% of attacks on your accounts.
Insurance companies are starting to require multi-factor authentication for everything and will not honor claims by parties who don’t have it implemented.
Next-Generation Firewalls & Antivirus
What is it?
Next-generation firewalls and antivirus software are more advanced versions of the traditional versions. If your business is still using a traditional antivirus software, your vulnerable to cyberattacks.
They still have some of the old protection capabilities, but they add additional layers of protection to help keep your network secure.
Next-generation firewalls add the ability to filter packets based on applications. They have integrated intrusion prevention, deep packet inspection, and cloud-delivered threat intelligence.
Next-Generation antivirus takes a proactive approach by using a Managed Threat Response service that eliminates problems before they arise.
While traditional antivirus takes a reactive approach by responding to an attack after it already happened.
Why is it important?
Next-generation firewalls and antivirus software help prevent cyber attacks and threats before they have a chance to get inside your network.
The next-gen versions will help to keep your business networks and data secure.
Advanced Endpoint Defense
What is it?
This security product lives on workstations, servers, and likely mobile phones and IoT devices where applicable.
It is often described anti-virus 2.0 as it incorporates anti-virus principles but extends into assisting with investigation, enabling rollback or response to a threat as well as assisting with data leak protection.
These tools are often paired with a security operations center (SOC) to ensure response times can meet today’s threats.
Some higher-end tools assist with threat hunting through this SOC as well as perform vulnerability management.
You will often hear the terms endpoint detection and response (EDR), managed detection and response (MDR), or extended detection and response (XDR) as references.
Why is it important?
Today’s threats cannot be ignored and need investigation to ensure a persistent threat doesn’t exist on systems.
These tools also assist in helping prevent issues occurring through tighter controls on items such as network connections and USB devices.
Protective Filtering
What is it?
Protective filtering uses computers, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to automate the protection of environments by auditing the traffic or content being sent over the filter.
If the traffic meets a certain threshold, the traffic is then automatically handled by an action set by the administrator.
This can be a complete block of the traffic, quarantine or sandboxing, or simply logging and alerting the administrator that no automatic action was taken.
Why is it important?
The current threat landscape is based on humans being tricked into doing what an attacker wants. Sometimes these tactics can be difficult for the average user to discern from a legitimate transaction.
Protective filtering allows IT admins like ourselves, to block, quarantine, or log specific activity known to be harmful or lead to sites or servers controlled by threat actors.
Protective filtering should be used along with a security and awareness training program.
Patch Approval & Management
What is it?
Patch management is the process of distributing and applying updates to software.
These patches are often necessary to correct errors (vulnerabilities or “bugs”) in the software.
Common areas that will need patches include:
- Operating systems
- Applications
- Embedded systems (network equipment, switches and firewalls)
When a vulnerability is found after the release of a piece of software, a patch can be used to fix it. Doing so helps ensure that assets in your environment are not susceptible to exploitation.
Why is it important?
Patch management is important for the following key reasons:
Security: Patch management fixes vulnerabilities on your software and applications that are susceptible to cyber-attacks, helping your organization reduce its security risk.
System uptime: Patch management ensures your software and applications are kept up-to-date and run smoothly, supporting system uptime.
Compliance: With the continued rise in cyber- attacks, organizations are often required by regulatory bodies to maintain a certain level of compliance. Patch management is a necessary piece of adhering to compliance standards.
Feature changes: Patch management can go beyond software bug fixes to also include feature/functionality updates. Patches can be critical to ensuring that you have the latest and greatest that a product has to offer
Data Backup & Recovery
What is it?
Quite simply, backups are copies of your critical data, files and systems, physically and logically separated from your production data, files and systems.
Backup strategy is critical to ensure that in the event of a disruption, loss or encryption, backups are there to restore to normal operations.
Different systems, files and data sets have different levels of importance and value. Critical systems and data take priority in the race to restoration.
A commonly accepted practice is the 3-2-1-1 Backup Rule—3 copies of data, 2 different media to store backups, 1 offsite location to store backups online, and 1 offsite location to store backups offline.
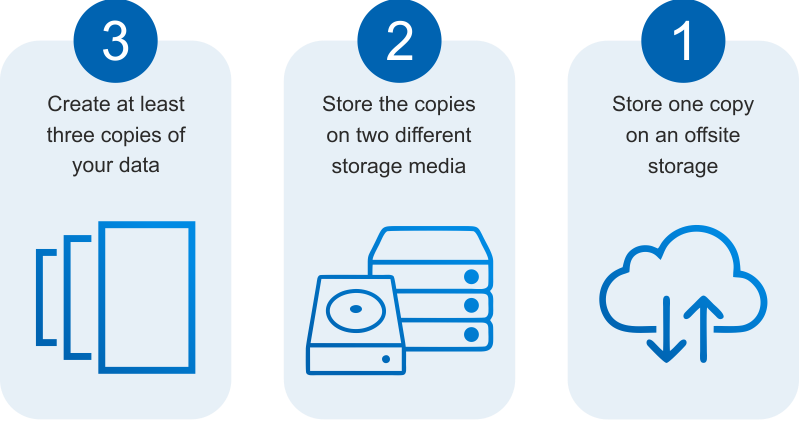
Equally important is testing. Regularly recurring test restores are a must. Know that you can restore your systems and data.
Why is it important?
Hope is not a contingency plan. Systems crash, physical disasters happen, and threat actors are constantly attacking.
A high percentage (up to 93%) of businesses fail within months of a major data loss. if they couldn’t restore to normal operations quickly.
Offline copies are a must as a final layer of defense against encryption/ ransomware attacks, as threat actors are known to compromise online backups long before they make their presence known to their victims.
In these cases, an offline (aka: “air-gapped”) backup is the only recourse in restoring your systems, files and data.
User Cyber Security Awareness Training
What is it?
No matter how hardened your IT infrastructure and cloud-based app security are, the weakest link is your people.
Training them to recognize threats is critical. Cyber security awareness training is a systematic, recurring process that flexes as threats advance and change.
Why is it important?
For your team members to do their jobs, they must have access to your assets. Once their credentials are compromised, threat actors have the same access.
They are being baited constantly. On a macro level, threat actors use social engineering tactics to get your team members to slip up.
On a micro level, threat actors are researching them specifically. They need to be aware of this and recognize it.
Who is covered by this training?
Providing this training for every team member in your organization is very important.
Consider vendors and contractors who have access to your facilities, communications systems, networks
and apps.
In your supply chain, every upstream and downstream contractor should have training in place. Make this mandatory. If they get compromised and have access to your assets, you’re now compromised.
Network Assessment
What is it?
This is a process of reviewing local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs) to inspect assets to help identify all resources on the network and assist in following best practices and industry standards.
Reports from network assessments are used to understand risk and to support improvements to the network and associated devices.
Why is it important?
In order to improve from a security perspective, it is valuable to know what needs to be needs to be improved.
A network assessment is a key component of understanding what has to be managed. Regular network assessments help demonstrate due diligence and a focus on continual improvement.
DNS Security
What is it?
Domain Name System (DNS) security provides an additional layer of protection between an employee and the internet by blacklisting dangerous sites and filtering out unwanted content.
Why is it important?
With remote and distributed workforces and digital business transformation driving consolidation of networking and security functions to the cloud, DNS security is more important than ever.
By using secure DNS servers both at home and at work, employees can avoid unnecessary risks and the potential for malicious attacks.
DNS servers can also be another vector of attack because an attacker could identify a vulnerability and take over or redirect the domain name to somewhere else or spoof it completely.
Dark Web Monitoring
What is it?
Dark web monitoring is the act of monitoring the part of the internet that is accessed through a Tor browser.
The dark web provides a layer of anonymity that attracts criminals who feel they can operate undetected.
There are 2 million active users who connect to the dark web through the Tor browser every day. An estimated 2% to 5% of the global GDP is laundered on the dark web annually.
Why is it important?
Dark web monitoring is essential for the following key reasons:
- The price for access to corporate networks increased by 61% in Q1 2020.
- Over Q1 2019, Cybercrime yields over $1.5 trillion in revenue per year.
- Information on 267 million Facebook users sold in Q1 2020 for just $540.
- In Q1 2020 alone, over 73.2 million new user records hit the dark web.
- About 164 million user records from a dozen major companies were exposed in a single Q1 2020 dump.
- 53% of organizations have had a data breach caused by third-party information theft.
While you can manually monitor the dark web by downloading a Tor browser and locating and joining various dark web forums, it isn’t feasible or efficient to do this for several reasons.
First, many dark web sites are hidden or unpublished to the public, and the search engine within the dark web does not function like the one on the surface web, like Google.
Second, many cybercriminals are very careful who they interact with, so establishing yourself as a trusted
entity on the dark web can prove challenging.
Here at bva, we have dark web monitoring tools to aid in these efforts, along with their own. These services dive deep into the corners of the dark web to look for potential risks to an organization.
They’ll monitor for new dark web threats to your systems and data 24/7/365 and quickly alert you to possible trouble, enabling you to stop cyberattacks before they start.








